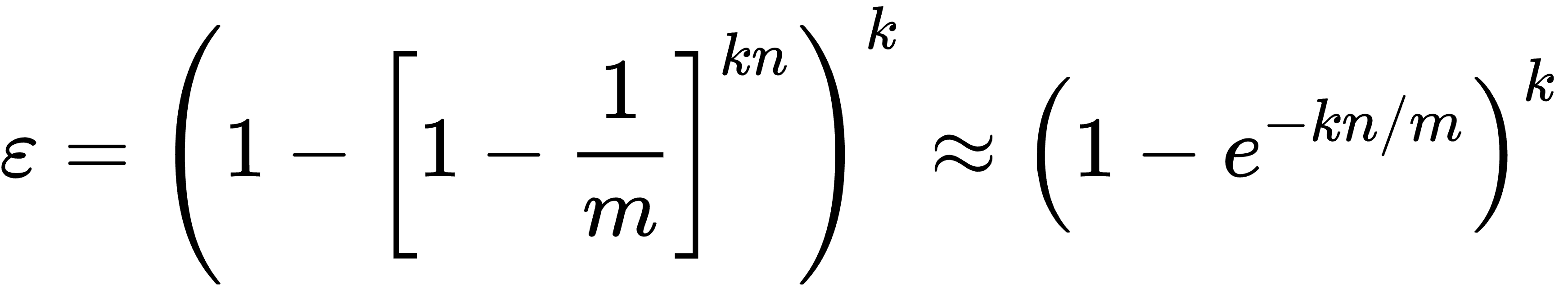前言
本文将以 C# 语言来实现一个简单的布隆过滤器,为简化说明,设计得很简单,仅供学习使用。
感谢@时总百忙之中的指导。
布隆过滤器简介
布隆过滤器(Bloom filter)是一种特殊的 Hash Table,能够以较小的存储空间较快地判断出数据是否存在。常用于允许一定误判率的数据过滤及防止缓存击穿及等场景。
相较于 .NET 中的 HashSet 这样传统的 Hash Table,存在以下的优劣势。
优势:
占用的存储空间较小。不需要像 HashSet 一样存储 Key 的原始数据。
劣势:
存在误判率,过滤器认为不存在的数据一定不存在,但是认为存在的数据不一定真的存在。这个和布隆过滤器的实现方式有关。
不支持数据的删除,下文会讲为什么不支持删除。
数据的存储#
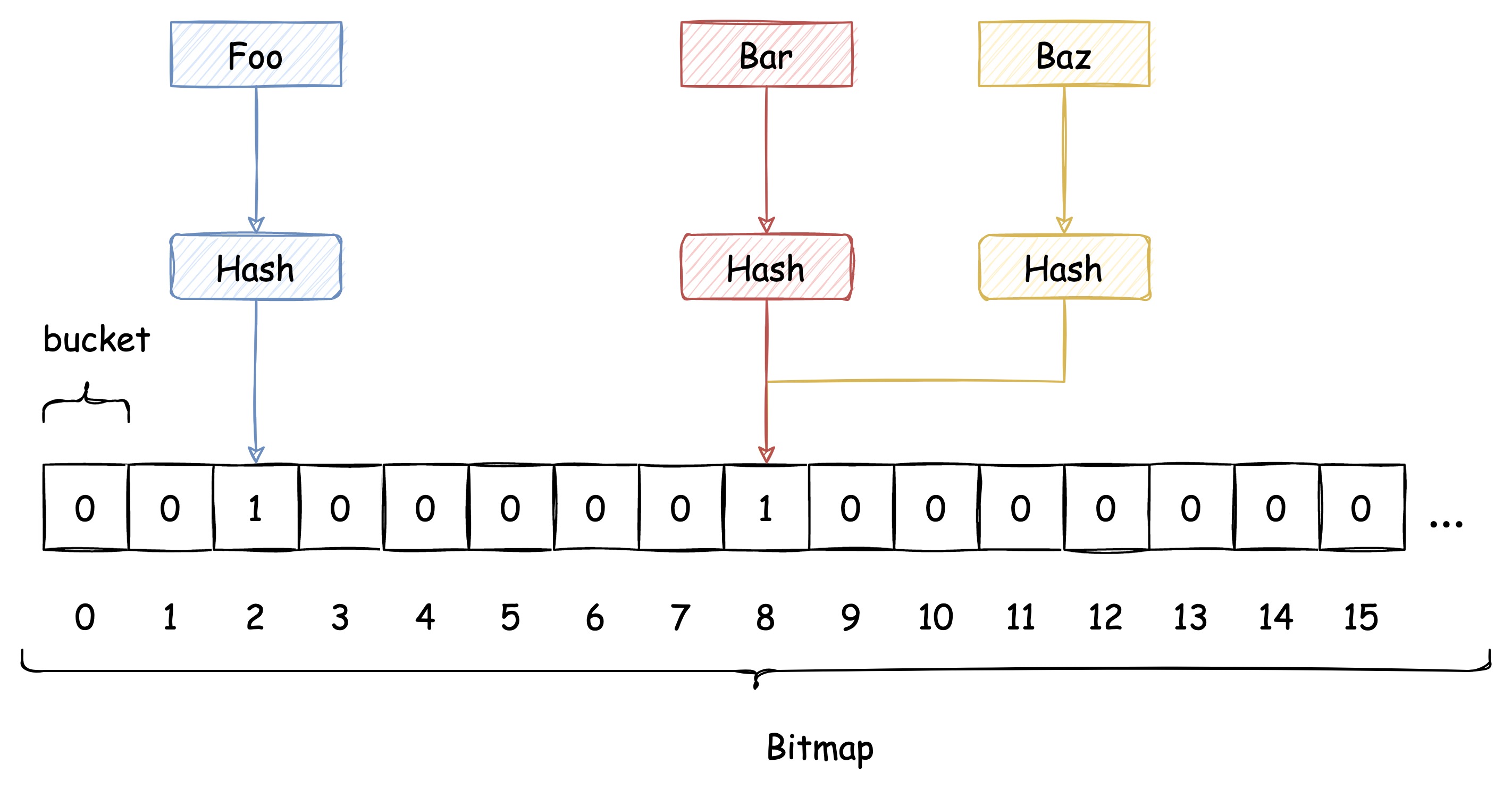
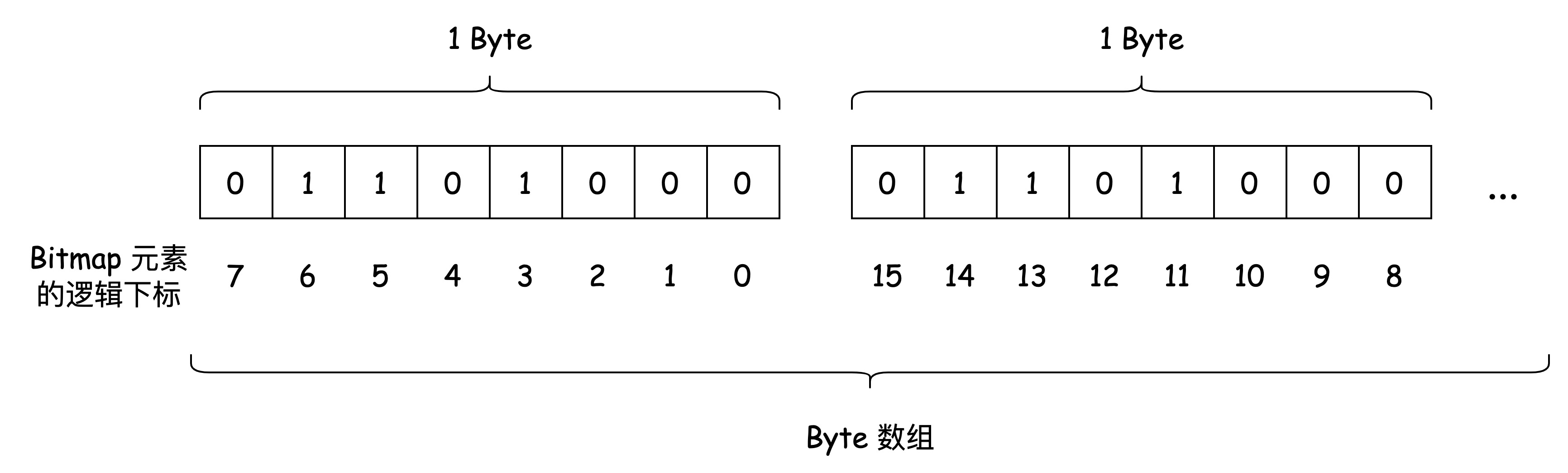
布隆过滤器的数据保存在 位图(Bitmap)上。Bitmap 简而言之是二进制位(bit)的数组。Hash Table 保存每个元素的位置,我们称之为 桶(bucket), Bitmap 上的每一位就是布隆过滤器的 bucket。
布隆过滤器的每一个 bucket 只能存储 0 或 1。数据插入时,布隆过滤器会通过 Hash 函数计算出插入的 key 对应的 bucket,并将该 bucket 设置为 1。
查询时,再次根据 Hash 函数计算出 key 对应的 bucket,如果 bucket 的值是 1,则认为 key 存在。
Hash 冲突的解决方案#
布隆过滤器使用了 Hash 函数,自然也逃不过 Hash 冲突的问题。对布隆过滤器而言,发生 Hash 冲突也就意味着会发生误判。
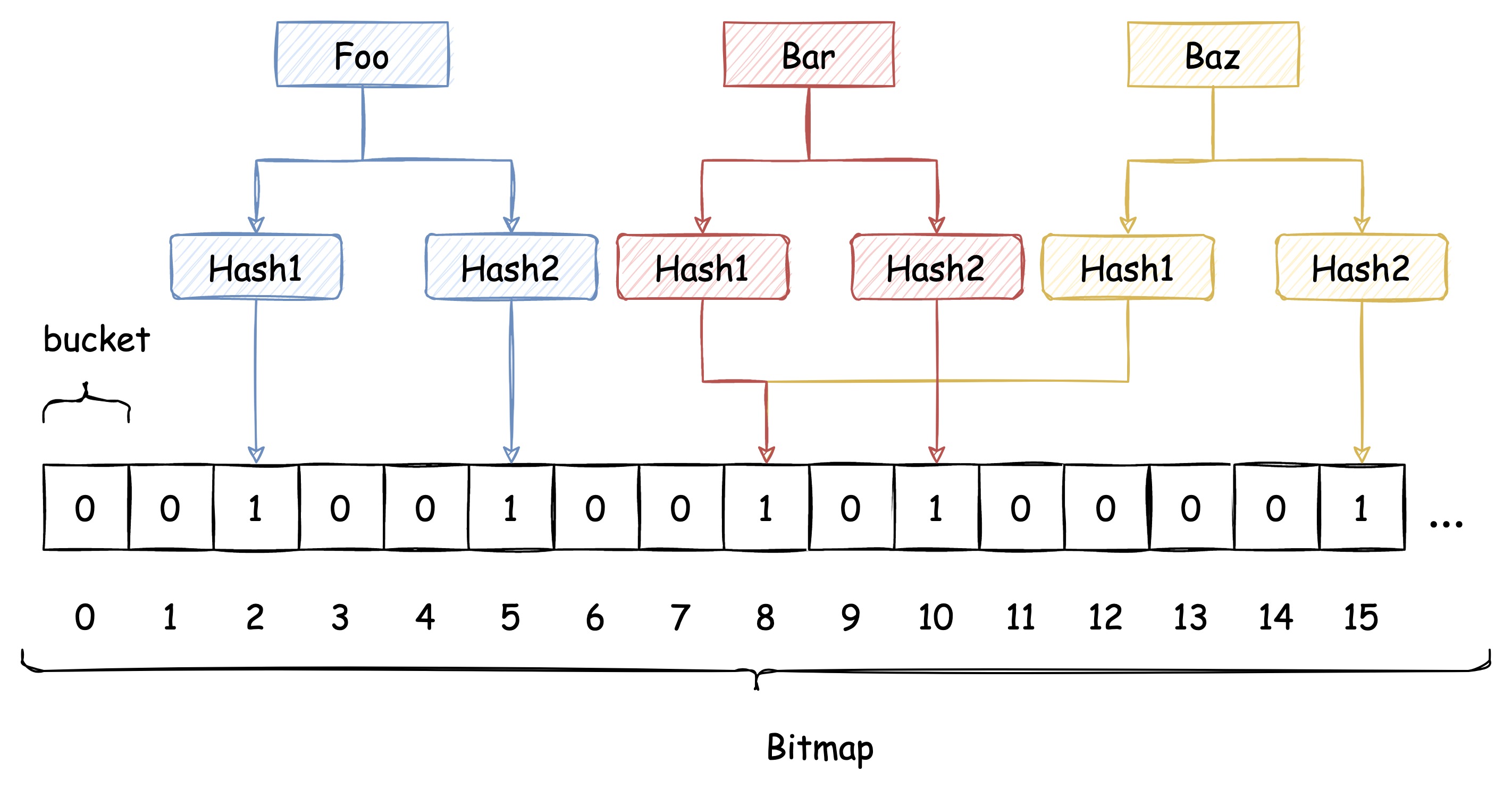
传统 Hash 算法解决 Hash 冲突的方式有 开放定址法、链表法等。而布隆过滤器解决 Hash 冲突的方式比较特殊,它使用了多个 Hash 函数来解决冲突问题。
下图中插入布隆过滤器的 Bar 和 Baz 经过 Hash1 计算出的位置是同一个,但 Hash2 计算出的位置是不一样的,Bar 和 Baz 得以区分。
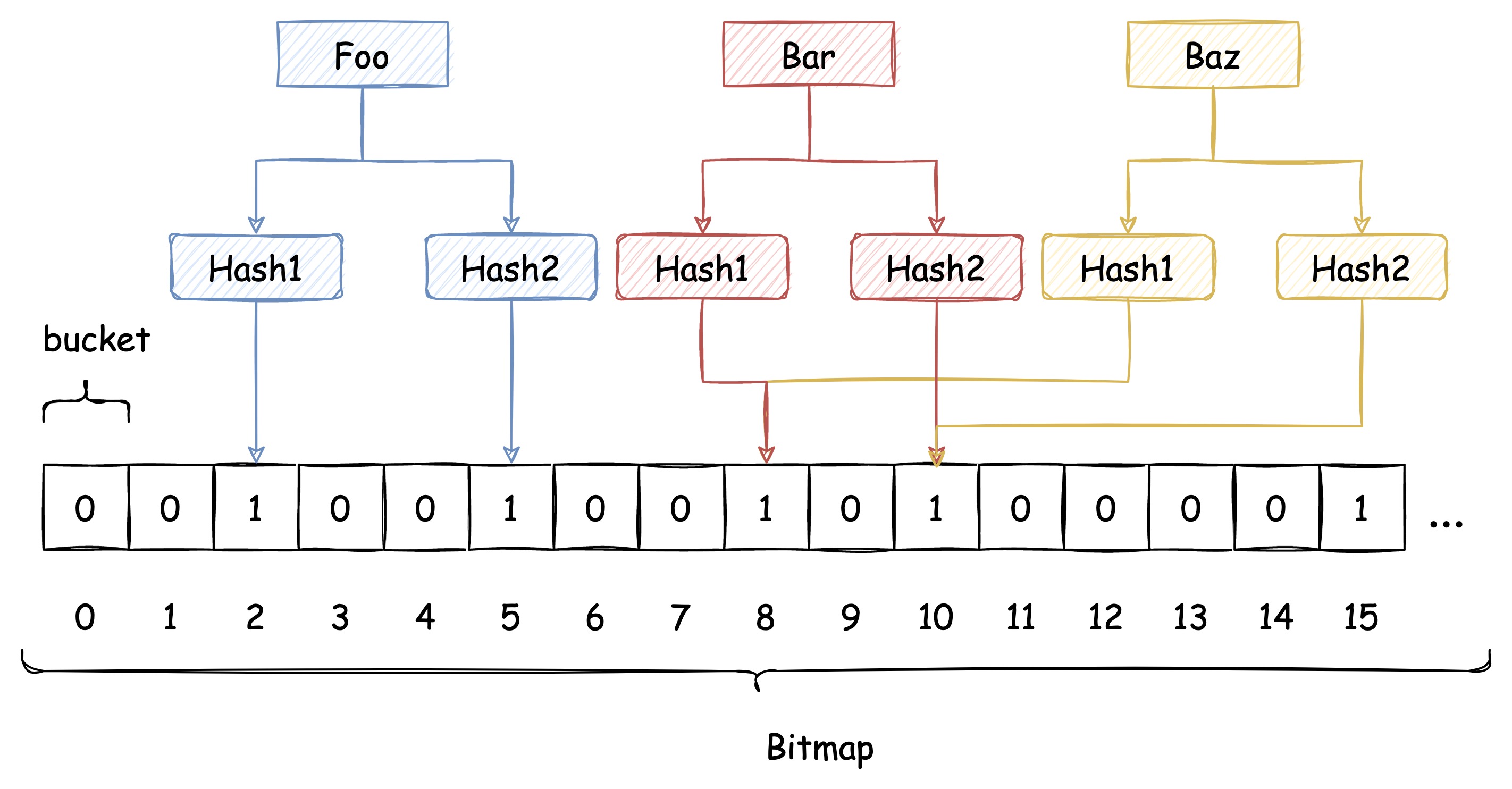
即使布隆过滤器使用了这种方式来解决 Hash冲突,冲突的可能性依旧存在,如下图所示:
由于布隆过滤器不保留插入的 Key 的原始值,Hash 冲突是无法避免的。我们只能通过增加 Hash 函数的数量来减少冲突的概率,也就是减少误判率。
假设布隆过滤器有 m 个 bucket,包含 k 个哈希函数,已经插入了 n 个 key。经数学推导可得误判率 ε 的公式如下:
具体推断过程可参考 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bloom_filter。
布隆过滤器的误判概率大致和 已经插入的 key 的数量 n 成正比,和 hash函数数量 k、bucket 数 m 成反比。为了减少误判率,我们可以增加 m 或 增加 k,增加 m 意味着过滤器占用存储空间会增加,增加 k 则意味着插入和查询时的效率会降低。
为什么布隆过滤器不支持删除#
布隆过滤器通过多个 Hash 函数来解决冲突的设计,也意味着多着插入元素可能会共享同样的 bucket,删掉一个元素的同时,也会被其他元素的一部分 bucket 给删掉。因此基于 Bitmap 实现的布隆过滤器是不支持删除的。
用 C# 实现 Bitmap
在实现布隆过滤器之前,我们首先要实现一个 Bitmap。
在 C# 中,我们并不能直接用 bit 作为最小的数据存储单元,但借助位运算的话,我们就可以基于其他数据类型来表示,比如 byte。下文用 byte 作为例子来描述 Bitmap 的实现,但不仅限于 byte,int、long 等等也是可以的。
位运算#
下面是 C# 中位运算的简单介绍:
| 符号 | 描述 | 运算规则 |
|---|---|---|
| & | 与 | 两个位都为1时,结果才为1 |
| | | 或 | 两个位都为0时,结果才为0 |
| ^ | 异或 | 两个位相同为0,相异为1 |
| ~ | 取反 | 0变1,1变0 |
| << | 左移 | 各二进位全部左移若干位,低位补0 |
| >> | 右移 | 各二进位全部右移若干位,高位补0 |
一般来说,我们要进行位运算计算的数据通常都是由多个二进位组成的。对两个数字使用 &、|、^ 这三个运算符时,需要对齐两个数字的右边,一位位地进行计算。
// 0b 代表值用二进制表示数字short a = 0b0111111111111001;byte b = 0b011111111;short c = (short)(a & b); // 0b0111111111111001short d = (short)(a | b); // 0b0111111111111111short e = (short)(a ^ b); // 0b0000000000000110byte f = (byte)~b; 0b011111111;short g = (short)(b << 1); // 0b0000000111111111;short h = (short)(b >> 1); // 0b0000000001111111;
利用位运算创建 Bitmap#
借助 byte 实现 Bitmap,也就是要能够修改和查看 byte 上的每一个 bit 的值,同时,修改要能够实现幂等。
指定位设置成 1
按前面说的位运算的规则,是不能够单独修改 bit 序列中某一位的。位运算需要从右到左一对对计算。
使用|可以实现这个功能。假设我们要改变从右开始下标为 3(初始位置0) 的 bit 的值,则需要准备一个该位置为 1,其他位置都是 0 的 bit 序列,与要改变的 bit 序列进行|运算。
// 为了将 a 的右边数起第 3 位改成 1,需要准备一个 bbyte a = 0b010100010;byte b = 1 << 3; // 0b000001000a |= b; // 0b010101010
指定位设置成 0
和设置成 1 正好相反,需要准备一个指定位置为 0,其他位置都是 1 的 bit 序列,与要改变的 bit 序列进行&运算。
byte a = 0b010101010;byte b = 1 << 3; // 0b000001000b = ~b; // 0b111110111a &= b; // 0b010100010
查看指定位的值
利用 & 运算符,只要计算结果不为 0,就代表指定位置的值为 1。
byte a = 0b010101010;byte b = 1 << 3; // 0b000001000;a &= b; // 0b000001000;
了解了基本的操作之后,我们把数据存储到 byte 数组上。
class Bitmap{ private readonly byte[] _bytes; private readonly long _capacity; public Bitmap(long capacity) { _capacity = capacity; _bytes = new byte[_capacity / 8 + 1]; } public long Capacity => _capacity; public void Set(long index) { if (index >= _capacity) { throw new IndexOutOfRangeException(); } // 计算出数据存在第几个 byte 上 long byteIndex = index / 8; // 计算出数据存在第几个 bit 上 int bitIndex = (int)(index % 8); _bytes[byteIndex] |= (byte)(1 << bitIndex); } public void Remove(long index) { if (index >= _capacity) { throw new IndexOutOfRangeException(); } long byteIndex = index / 8; int bitIndex = (int)(index % 8); _bytes[byteIndex] &= (byte)~(1 << bitIndex); } public bool Get(long index) { if (index >= _capacity) { throw new IndexOutOfRangeException(); } long byteIndex = index / 8; int bitIndex = (int)(index % 8); return (_bytes[byteIndex] & (byte)(1 << bitIndex)) != 0; }}用 C# 实现 布隆过滤器
有了 Bitmap,我们再把 Hash 函数的实现准备好,一个简单的布隆过滤器就可以完成了。这里,我们参考 guava 这个 java 库的实现。
https://github.com/google/guava/blob/master/guava/src/com/google/common/hash/BloomFilter.java
MurmurHash3 的使用#
我们使用和 guava 一样的 MurmurHash3 作为 Hash 函数的实现。
下面是笔者在 github 上找到的一个可用实现。
https://github.com/darrenkopp/murmurhash-net
使用这个库,我们可以将任意长的 byte 数组转换成 128 位的二进制位,也就是 16 byte。
byte[] data = Guid.NewGuid().ToByteArray(); // returns a 128-bit algorithm using "unsafe" code with default seedHashAlgorithm murmur128 = MurmurHash.Create128(managed: false);byte[] hash = murmur128.ComputeHash(data);
将任意类型的 key 转换为 byte 数组#
Funnel 与 Sink 的定义#
我们需要将各种类型 key 转换成 MurmurHash 能够直接处理的 byte 数组。为此我们参考 guava 引入下面两个概念:
Funnel:将各类数据转换成 byte 数组,包括 int、bool、string 等built-in 类型及自定义的复杂类型。
Sink:Funnel 的核心组件,作为数据的缓冲区。Funnel 在将自定义的复杂类型实例转换成 byte 数组时,就需要将数据拆解分批写入 sink。
Funnel 可以定义成如下的委托,接受原始值,并将其写入 sink 中。
delegate void Funnel<in T>(T from, ISink sink);
Sink 将不同类型的数据转换成 byte 数组并汇总到一起。
interface ISink{ ISink PutByte(byte b); ISink PutBytes(byte[] bytes); ISink PutBool(bool b); ISink PutShort(short s); ISink PutInt(int i); ISink PutString(string s, Encoding encoding); ISink PutObject<T>(T obj, Funnel<T> funnel); /// ... 其他 built-in 类型,读者可自行补充}简单的 Funnel 实现如下所示:
public class Funnels{ public static Funnel<string> StringFunnel = (from, sink) => sink.PutString(from, Encoding.UTF8); public static Funnel<int> IntFunnel = (from, sink) => sink.PutInt(from);}自定义复杂类型的 Funnel 实现则可以数据拆解分批写入 sink。复杂类型的实例成员依旧可能是复杂类型,因此我们要在 Sink 上实现一个 PutObject 来提供套娃式拆解。
Funnel<Foo> funnelFoo = (foo, sink) =>{ sink.PutString(foo.A, Encoding.UTF8); sink.PutInt(foo.B); Funnel<Bar> funnelBar = (bar, barSink) => barSink.PutBool(bar.C); sink.PutObject(foo.Bar, funnelBar);};class Foo{ public string A { get; set; } public int B { get; set; } public Bar Bar { get; set; }}class Bar{ public bool C { get; set; }}Sink 的实现#
Sink 的核心是 byte 数组缓冲区的实现,利用 ArrayPool 我们可以很方便的实现一个 ByteBuffer。
class ByteBuffer : IDisposable{ private readonly int _capacity; private readonly byte[] _buffer; private int _offset; private bool _disposed; public ByteBuffer(int capacity) { _capacity = capacity; _buffer = ArrayPool<byte>.Shared.Rent(capacity); } public void Put(byte b) { CheckInsertable(); _buffer[_offset] = b; _offset++; } public void Put(byte[] bytes) { CheckInsertable(); bytes.CopyTo(_buffer.AsSpan(_offset, bytes.Length)); _offset += bytes.Length; } public void PutInt(int i) { CheckInsertable(); BinaryPrimitives.WriteInt32BigEndian(GetRemainingAsSpan(), i); _offset += sizeof(int); } public void PutShort(short s) { CheckInsertable(); BinaryPrimitives.WriteInt32BigEndian(GetRemainingAsSpan(), s); _offset += sizeof(short); } // ... 其他的 primitive type 的实现 public Span<byte> GetBuffer() => _buffer.AsSpan(.._offset); public bool HasRemaining() => _offset < _capacity; public void Dispose() { _disposed = true; ArrayPool<byte>.Shared.Return(_buffer); } private void CheckInsertable() { if (_disposed) { throw new ObjectDisposedException(typeof(ByteBuffer).FullName); } if (_offset >= _capacity) { throw new OverflowException("Byte buffer overflow"); } } private Span<byte> GetRemainingAsSpan() => _buffer.AsSpan(_offset..);}Sink 则是对 ByteBuffer 的进一步封装,来适配当前使用场景。
class Sink : ISink, IDisposable{ private readonly ByteBuffer _byteBuffer; /// <summary> /// 创建一个新的 <see cref="Sink"/> 实例 /// </summary> /// <param name="expectedInputSize">预计输入的单个元素的最大大小</param> public Sink(int expectedInputSize) { _byteBuffer = new ByteBuffer(expectedInputSize); } public ISink PutByte(byte b) { _byteBuffer.Put(b); return this; } public ISink PutBytes(byte[] bytes) { _byteBuffer.Put(bytes); return this; } public ISink PutBool(bool b) { _byteBuffer.Put((byte)(b ? 1 : 0)); return this; } public ISink PutShort(short s) { _byteBuffer.PutShort(s); return this; } public ISink PutInt(int i) { _byteBuffer.PutInt(i); return this; } public ISink PutString(string s, Encoding encoding) { _byteBuffer.Put(encoding.GetBytes(s)); return this; } public ISink PutObject<T>(T obj, Funnel<T> funnel) { funnel(obj, this); return this; } public byte[] GetBytes() => _byteBuffer.GetBuffer().ToArray(); public void Dispose() { _byteBuffer.Dispose(); }}k 个 Hash 函数与 布隆过滤器 实现#
上文提到了 布隆过滤器 通过 k 个 hash 函数来解决 hash 冲突问题。实践中,我们可以把一次 murmur hash 的计算结果(16 byte)拆分为两部分并转换为 long 类型(一个 long 是 8 byte)。
这两部分结果分别保存到 hash1 和 hash2,第 k 个 hash 函数是对 hash1 和 hash2 的重新组合。
hash(k) = hash1 + (k-1) * hash2
public class BloomFilter<T>{ private readonly int _hashFunctions; private readonly Funnel<T> _funnel; private readonly int _expectedInputSize; private readonly Bitmap _bitmap; private readonly HashAlgorithm _murmur128; /// <summary> /// 创建一个新的 <see cref="BloomFilter"/> 实例 /// </summary> /// <param name="funnel">与插入元素类型相关的<see cref="Funnel"/>的实现</param> /// <param name="buckets">BloomFilter 内部 Bitmap 的 bucket 数量,越大,误判率越低</param> /// <param name="hashFunctions">hash 函数的数量,越多,误判率越低</param> /// <param name="expectedInputSize">预计插入的单个元素的最大大小</param> public BloomFilter(Funnel<T> funnel, int buckets, int hashFunctions = 2, int expectedInputSize = 128) { _hashFunctions = hashFunctions; _funnel = funnel; _expectedInputSize = expectedInputSize; _bitmap = new Bitmap(buckets); _murmur128 = MurmurHash.Create128(managed: false); } public void Add(T item) { long bitSize = _bitmap.Capacity; var (hash1, hash2) = Hash(item); long combinedHash = hash1; for (int i = 0; i < _hashFunctions; i++) { _bitmap.Set((combinedHash & long.MaxValue) % bitSize); combinedHash += hash2; } } public bool MightContains(T item) { long bitSize = _bitmap.Capacity; var (hash1, hash2) = Hash(item); long combinedHash = hash1; for (int i = 0; i < _hashFunctions; i++) { if (!_bitmap.Get((combinedHash & long.MaxValue) % bitSize)) { return false; } combinedHash += hash2; } return true; } [MethodImpl(MethodImplOptions.AggressiveInlining)] private (long Hash1, long Hash2) Hash(T item) { byte[] inputBytes; using (var sink = new Sink(_expectedInputSize)) { sink.PutObject(item, _funnel); inputBytes = sink.GetBytes(); } var hashSpan = _murmur128.ComputeHash(inputBytes).AsSpan(); long lowerEight = BinaryPrimitives.ReadInt64LittleEndian(hashSpan.Slice(0,8)); long upperEight = BinaryPrimitives.ReadInt64LittleEndian(hashSpan.Slice(8,8)); return (lowerEight, upperEight); }}扩展
带计数器的布隆过滤器#
上文讲到基于 Bitmap 实现的布隆过滤器不支持删除,但如果把 Bitmap 这个 bit 数组换成 n 个 bit 作为一个bucket的数组,那单个 bucket 就具备了计数能力。这样删掉一个元素的时候,就是在这个计数器上减一,借此能够在有限的范围内实现带删除功能的布隆过滤器,代价是,存储空间会变成原来的 n 倍。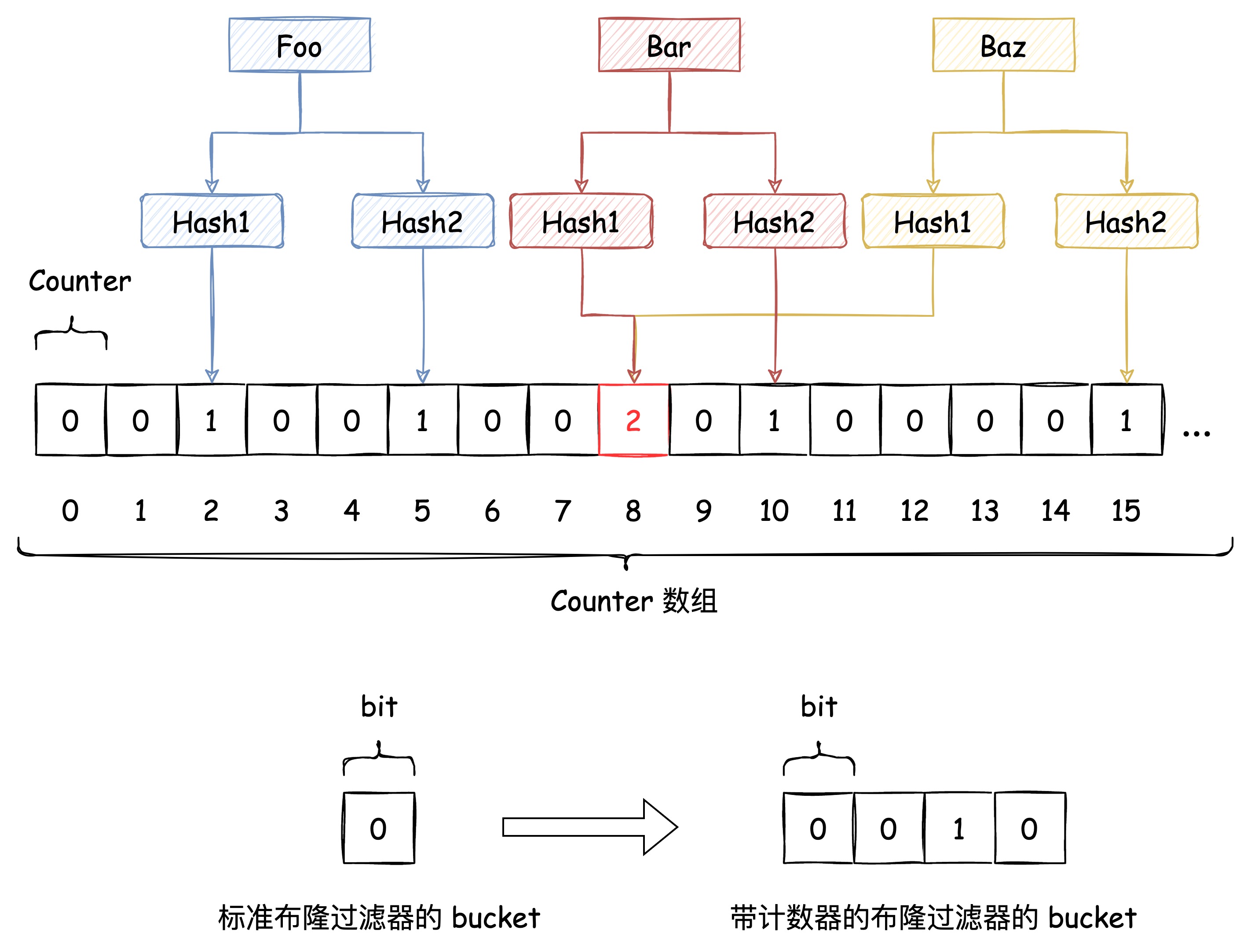
分布式布隆过滤器实现方案#
如果你有布隆过滤器的实际使用需求,并且是在分布式环境,笔者推荐下面这个库,它是作为 redis 的插件提供的,详情点击下方链接。
https://github.com/RedisBloom/RedisBloom
代码地址
为方便学习,本文所有的代码均已整理在 github:https://github.com/eventhorizon-cli/EventHorizon.BloomFilter